Exploring IGBT Modules in Power Electronics: Key Part Numbers, Applications and Specifications
IGBTs are essential in power electronics, bridging the gap between high efficiency and compact design. These semiconductor parts enable power conversion across industries, including automotive, renewable energy, industrial machinery, and more. In this article, we’ll explore leading IGBT modules from renowned manufacturers, their application benefits, technical specifications, and considerations for engineers and purchasing teams.
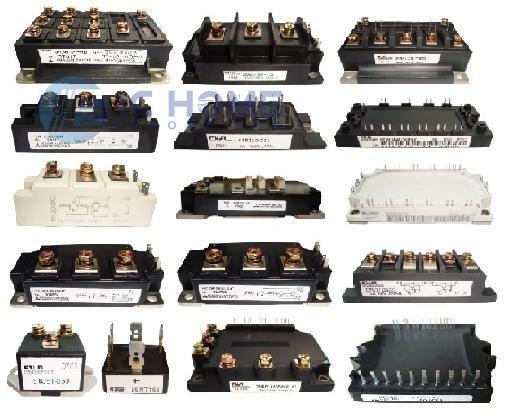

Key IGBT Parts for High-Efficiency Applications
Infineon TRENCHSTOP IGBT7: Reduced switching losses, this module targets consumer and industrial inverter applications. It is also suitable for motor control, ensuring high performance in a compact design.
Mitsubishi CM600DU-24NFH: This module offers enhanced thermal stability, which is essential for electric vehicles (EVs) and industrial machinery.
Fuji Electric P637 Series: Designed for renewable energy applications, this series improves the power factor and ensures stability in photovoltaic inverters.
Applications and Technical Insights into IGBT Modules
Applications Across Industries
IGBTs play a vital role across various industries, each with specific demands:
Automotive: In EVs, IGBTs are crucial for traction inverters that manage motor speed and efficiency. Their high current-carrying capacity ensures that EVs achieve rapid acceleration with minimal heat generation.
Renewable Energy: For solar inverters and wind turbines, IGBTs provide the efficiency needed for large power conversions. Advanced IGBT modules allow seamless energy transfer, increasing system stability and ensuring reliable energy output.
Industrial Motor Drives: In manufacturing, IGBTs are essential in motor drives that control equipment speed. They allow precise modulation of high-power motors, which is vital for automation and large machinery.
Consumer Electronics: Compact IGBT modules are used in air conditioners, refrigerators, and other high-power appliances where efficient energy management is critical.
Technical Specifications to Consider
When selecting an IGBT module, engineers and procurement teams should evaluate the following specifications:
Voltage and Current Ratings: IGBT modules are available in various voltage and current ratings, from 600V/50A for small consumer applications to 1200V/600A for industrial systems.
Switching Frequency: High-frequency switching is essential in applications where fast response times are necessary, such as motor control and inverter circuits.
Thermal Resistance: Effective heat dissipation is vital for the longevity of IGBT modules. Models with optimized thermal resistance allow for stable operation under high temperatures, which is particularly crucial in EVs and heavy-duty industrial applications.
Types of Packages and Their Importance
IGBT modules are available in different packaging formats, which influence the overall design and thermal management of the application:
Standard Package (Single-Phase): Often used in consumer and small-scale industrial applications, standard packages are compact and fit within restricted spaces.
Dual-In-Line Package (DIP): DIP packages are suitable for high-power modules that require enhanced thermal management. These are common in automotive and industrial sectors.
Integrated Power Module (IPM): IPM packages integrate IGBT and driver circuitry, simplifying the design process. These are prevalent in motor drives and HVAC systems for optimized energy consumption.
Each package type impacts the module’s heat dissipation capacity, which in turn affects the durability and efficiency of the system.
Choosing the Right IGBT Module for Your Application
Selecting the right IGBT module depends on factors such as application requirements, operational environment, and long-term efficiency goals. Key considerations include:
Application Voltage: High-voltage modules (above 1200V) are best for industrial and renewable applications, while medium-voltage modules are ideal for consumer electronics.
Power Loss Management: Reducing power loss during switching is crucial for high-efficiency applications. Modern IGBT models, like Infineon’s TRENCHSTOP and Fuji’s P637, offer minimized switching losses, which helps manage heat and improves longevity.
Temperature and Thermal Management: In applications like EVs and industrial motor drives, effective heat management ensures that IGBTs perform optimally over longer periods.
Conclusion
The landscape of IGBT modules continues to evolve, with manufacturers pushing the boundaries of efficiency and application diversity. By understanding these manufacturers’ offerings and carefully considering technical specifications such as voltage, current, and thermal resistance, procurement teams and engineers can make informed decisions for optimal power management in their systems. As IGBT modules advance, the focus remains on creating adaptable, high-performance solutions that meet the demands of today’s dynamic power electronics landscape.
For more information or to request a quote, please feel free to send us an RFQ.